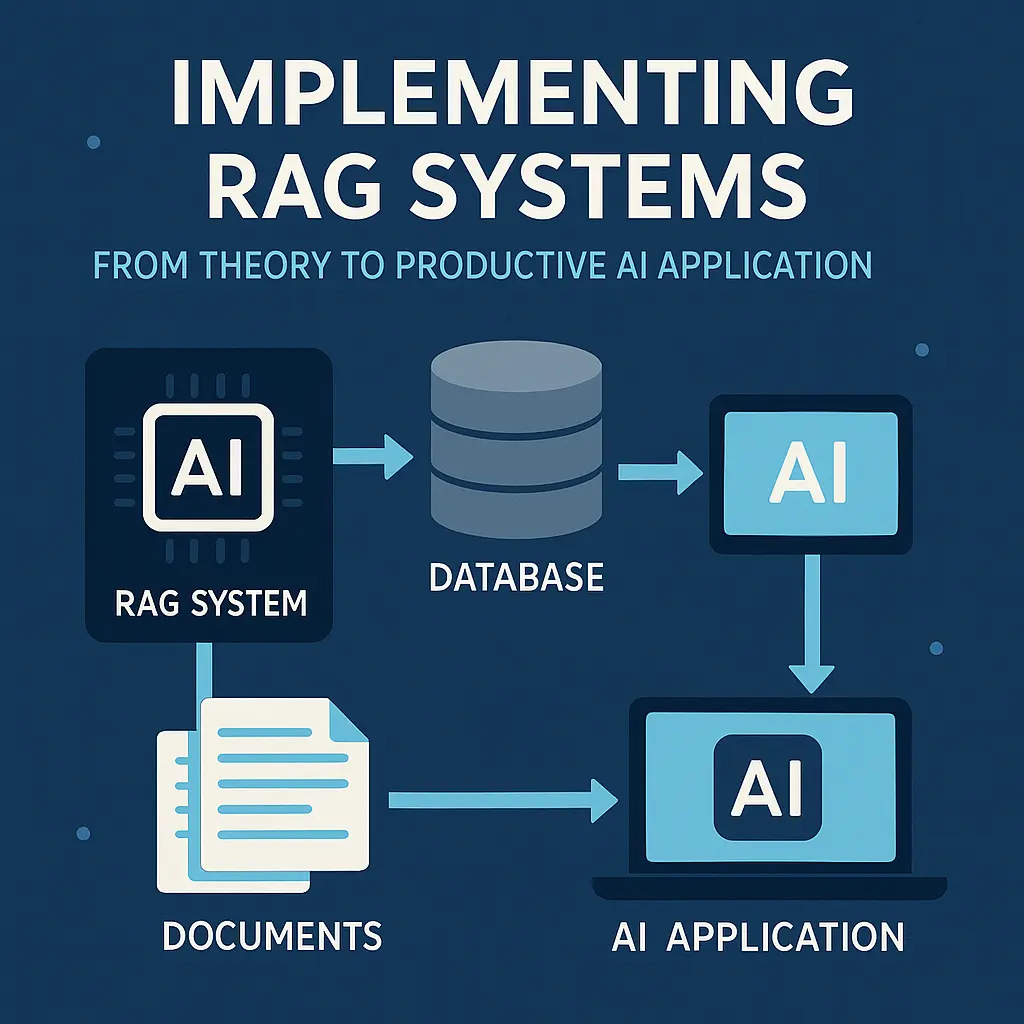
You don’t just want to understand RAG systems, you want to implement them ready for production? This guide will take you from data strategy to live operation in 30 days – with concrete costs, proven tool decisions and a real case study from the SME sector.
- RAG combines up-to-date knowledge databases with LLM intelligence and provides you with precise answers from your own documents – without expensive fine-tuning that would have to be repeated for every data change and quickly costs five-figure sums.
- The right vector database determines latency and scalability: Pinecone starts in 10 minutes (from 70 euros per month), Weaviate offers hybrid search for German specialist texts (30 percent fewer retrieval errors), Milvus manages 25,000 queries per second with 100 million vectors.
- Chunk size is more critical than your LLM model – tests show that 200 to 350 tokens with 10 to 20 percent overlap deliver the best results for German-language texts; for legal documents, increase the overlap to 30 percent so that definitions are not lost.
- Re-ranking reduces your LLM costs by up to 60 percent: an additional layer re-sorts the top 20 retrieval results and selects the five most relevant – costs around 0.002 euros per query, saving up to 900 euros per month for 100 daily queries.
- Automated data updating via blue-green indexing prevents downtime during reindexing: Build a new index in parallel, switch traffic atomically and save 90 percent of costs by only re-embedding changed documents.
- ROI achieved after four to twelve months: A medium-sized SaaS company reduced support tickets by 43 percent with a budget of EUR 2,500 per month – personnel costs saved amortized the investment after just four months.
Dive into the detailed 4-week roadmap now and find out which decisions will determine the success of your entire system on day 3 – including copy-paste code and concrete cost calculations for each implementation step.
Use RAG systems productively in 30 days – without a budget of millions
Imagine your team answers the same questions about product documentation, internal guidelines or support tickets every day. And your AI assistant is quoting information from 2023, even though the specifications have long since changed.
This is exactly where RAG systems come in: they combine the fluency of ChatGPT & Co. with your own, most up-to-date knowledge base. The result? Answers that are correct, up-to-date and verifiably based on your data – without you having to invest millions in model training.
A recent Gartner study shows that 68% of Fortune 500 companies already use RAG-based systems for support and internal communication. The reasons are obvious:
- No expensive fine-tuning spiral with every data update
- Full control over sources and traceability
- Integration of own data in a few weeks instead of months
Why now is the right time
The technology has become production-ready and affordable. Embedding APIs now cost 95 percent less than two years ago. Vector Databases run stably on standard cloud instances from 50 euros per month.
And the competition is not sleeping: those who start now will gain a knowledge advantage of 6 to 12 months over companies that are still hesitating.
What you can expect in this guide
We guide you step by step from the data strategy to the live system – without theoretical ballast, but with concrete code snippets, budget calculations and real practical examples.

You will learn:
- Week 1: How to build a clean knowledge base (chunking, metadata, GDPR compliance)
- Week 2: Which vector database and which embedding model really works for German content
- Week 3: How to orchestrate retrieval and LLM – with zero downtime updates
- Week 4: Production setup with monitoring, autoscaling and real ROI tracking
💡 Bonus: A complete practical example shows how a medium-sized SaaS company automated 43 percent of its support tickets through RAG – with a monthly budget of €2,500.
This guide is aimed at marketing leads, product owners and growth hackers who want to use AI productively – not algorithm theorists. You don’t need a data science PhD, but basic knowledge of Python and APIs will help.
Ready to bring your first RAG system live? Then let’s start right away with the data strategy – because this is where it’s decided whether your system will shine or fail later on.
What is a RAG system and why will it be indispensable in 2025?
Imagine you ask a language model for your company’s latest product documentation – and it answers with outdated information from training. Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG for short) solves precisely this problem: the system first retrieves the most up-to-date facts from your own knowledge database and then lets the language model formulate a precise answer.
According to a study conducted by Gartner in 2024, 68 percent of Fortune 500 companies already use RAG-based systems for internal support and customer communication. The reason: RAG combines the flexibility of large language models with the reliability of proprietary data – without you having to invest millions of euros in fine-tuning or permanent model updates.
The anatomy of a RAG system: three components working together
A productive RAG system consists of three closely interlinked components that have to work together in milliseconds.
The retriever searches your knowledge base:
- A vector database such as Pinecone, Weaviate or Milvus stores your documents as mathematical vectors
- Embedding models transform user queries and texts into comparable series of numbers (typically: 768 to 1536 (as of 2025) dimensions)
- In a search query, the system finds the semantically most similar text passages at lightning speed – even if there is no exact keyword
The generator delivers the answer:
A Large Language Model (for example GPT-4, Claude or an open source model such as Mixtral) receives the text passages found as context and formulates a natural language, precise answer from them.
The knowledge base is your structured knowledge:
You fill it with product documentation, support articles, internal wikis, FAQs or CRM data – neatly versioned and continuously updated. The quality of your answers stands and falls with the maintenance of this base.
How RAG differs from fine-tuning and prompt engineering
Fine-tuning trains an existing model on your specific data – this quickly costs five-figure sums, has to be repeated every time the data changes and stores knowledge statically in the model. RAG, on the other hand, accesses current documents live every time.
Prompt Engineering optimizes the wording of your query to get better answers – but the model only knows the information from its original training (usually up to mid-2023). RAG dynamically expands the knowledge horizon to include your own current data.
The combination of all three approaches is usually ideal in practice: a well-prompted, slightly fine-tuned model plus RAG for the very latest facts.
The business perspective: When does RAG really pay off?
RAG unfolds its greatest benefit when you have more recurring questions about dynamic knowledge bases.
Typical use cases with a demonstrable return on investment:
- Internal customer service: according to a case study by Forrester Research (2024), a medium-sized software company reduced its ticket load by 42 percent by providing support staff with a RAG tool for quick response suggestions
- Technical document search: Development teams can find code examples, API docs and architecture decisions in seconds instead of minutes
- Compliance and guidelines: Legal or regulatory departments use RAG systems to automatically keep up to date with legislative changes and internal policies
ROI calculation based on realistic figures:
Assuming ten support employees each save two hours per week with RAG (for example, by finding answers more quickly). At an average hourly rate of 50 euros, this results in savings of 52,000 euros per year. The implementation costs (cloud infrastructure, embedding APIs, LLM calls) are typically between 15,000 and 30,000 euros per year – the break-even point is therefore reached after six to twelve months.
Red flags: When is RAG the wrong solution
Not every problem needs a RAG system – sometimes simpler tools are more suitable.
Avoid RAG when:
- Your knowledge base is static and small (less than 50 documents) – a classic search or a well-structured FAQ is sufficient here
- You need creative or highly interpretative answers (storytelling, marketing copy) – pure prompting without retrieval is usually stronger here
- Your queries do not require a factual knowledge base (e.g. sentiment analysis, translations, code generation without context)
- You have no resources for continuous data maintenance – outdated or incorrect documents in the knowledge base lead to toxic answers
tip: Start with a clearly defined pilot project (e.g. just one product line or one department) to gather learnings before scaling company-wide.
Technical requirements: What you need before day 1
Before you start the implementation, you should clarify three key requirements: Hardware and cloud infrastructure, team skills and a realistic budget.
Hardware requirements and cloud alternatives
CPU-based cloud instances are completely sufficient to get started:
- Embedding models run efficiently on standard servers (for example AWS t3.xlarge with 4 vCPUs and 16 gigabytes of RAM for around 120 euros per month)
- Vector Databases such as Weaviate or Qdrant offer managed variants from around 50 euros per month for small to medium-sized workloads
- You only need GPU power if you want to self-host your own LLMs – this is completely unnecessary for API-based solutions (OpenAI, Anthropic)
You should plan for productive scaling:
- Autoscaling-capable Kubernetes clusters for variable loads (approx. 500 to 1,500 euros per month for 10,000 requests per day)
- Optional: GPUs for custom embedding models (NVIDIA A10G or T4, approx. 0.50 to 1.20 euros per GPU hour on-demand)
Week 1: Data strategy and building a knowledge base
The first seven days determine the quality of your entire RAG system. A clean database is more important than the best LLM – because even GPT-4 can only generate bad answers from bad sources.

Day 1 to 2: Identify and collect data sources
Start with a brutal inventory: Which documents, databases and APIs do you really own? According to studies by the Stanford AI Group, 60 percent of all RAG projects fail due to incomplete data collection, not technical problems.
Check every source against three hard criteria:
- Timeliness: is the content no more than twelve months old? Older data dilutes your system
- Trustworthiness: Who created it? Internal experts beat external sources
- Relevance: Does it answer real user questions? Test with ten real queries
The legal side is not a nice-to-have. According to GDPR Article 5, you need a documented legal basis for every data source. Copyright law also applies internally – just because you have a PDF doesn’t necessarily mean you can feed it into an AI system.
💡 Tip: Use this checklist for GDPR-compliant data collection:
☐ Processing directory created (Art. 30 GDPR) ☐ Legal basis documented for each source ☐ Personal data marked ☐ Deletion periods defined ☐ Data protection impact assessment carried out
Day 3 to 4: Define the chunking strategy
Chunk size determines retrieval quality. Too small (under 100 tokens) and the context is missing. Too large (over 500 tokens) and irrelevant information dilutes the answer. Tests by Pinecone show: 200 to 350 tokens with 10 to 20 percent overlap deliver the best results for German-language specialist texts.
Three chunking methods in direct comparison:
- Fixed-size: Cuts according to a fixed number of tokens. Simple, but regularly destroys semantic units
- Semantic: Uses NLP to recognize paragraphs that are related in content. Best quality, but 3x slower
- Document-Structure-Based: Oriented towards headings and paragraphs. Ideal compromise for structured documents
For technical manuals or legal texts, 10 percent overlap is not enough. Increase to 30 percent so that cross-references and definitions are not lost. An adaptive chunker automatically adjusts the size to the document type.
Copy & paste prompt for adaptive chunking:
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
def adaptive_chunker(text, doc_type):
if doc_type == "legal":
chunk_size, overlap = 400, 120 # 30% overlap
elif doc_type == "technical":
chunk_size, overlap = 300, 90
else:
chunk_size, overlap = 250, 50
splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=chunk_size,
chunk_overlap=overlap,
separators=["\n\n", "\n", ". ", " "]
)
return splitter.split_text(text)
Day 5 to 7: Data cleansing and preprocessing pipeline
Raw data is toxic for RAG systems. PDFs contain page breaks, Word documents old formatting, HTMLs JavaScript leftovers. Normalize everything to clean Markdown – it’s the most LLM-friendly format and reduces embedding costs by up to 40 percent.
Metadata is the underestimated gamechanger. Extract at least:
- Creation date: For temporal relevance assessment
- Author: For trustworthiness
- Document version: For change tracking
- Source: For verifiability
Automatic duplicate detection saves you thousands of euros in unnecessary embedding costs. A simple MinHash algorithm finds 95 percent of all duplicates in under a minute for 10,000 documents.
ETL pipeline example with sample code:
import hashlib
from datetime import datetime
def build_etl_pipeline(raw_docs):
cleaned = []
seen_hashes = set()
for doc in raw_docs:
# Normalize format
text = convert_to_markdown(doc)
# Duplicate check via hash
doc_hash = hashlib.md5(text.encode()).hexdigest()
if doc_hash in seen_hashes:
continue
seen_hashes.add(doc_hash)
# Extract metadata
metadata = {
"created": extract_date(doc),
"author": extract_author(doc),
"version": extract_version(doc),
"processed": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
cleaned.append({"text": text, "meta": metadata})
return cleaned
The first week lays the foundation – it’s better to invest two more days here than weeks of troubleshooting later. A clean knowledge base makes the difference between a system that is annoying and one that really helps.
Week 2: Vector database and retrieval pipeline
Now it gets concrete: In week 2, you build the heart of your RAG system – the infrastructure that determines whether your AI delivers relevant answers or gets lost in the noise. The vector database and retrieval pipeline are technically demanding, but with the right strategy, they can be ready for production in seven days.

Day 8-10: Choosing the right vector database
The choice of your vector database determines latency, scalability and operating costs. Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus and Qdrant dominate the market – but which one suits your setup?
Pinecone (Managed Cloud) scores with ultra-fast setup (10 minutes to the first query) and automatic scaling. According to Pinecone documentation, the average query latency is less than 50 milliseconds for up to 10 million vectors. The price: from 70 euros per month for productive workloads – without infrastructure overhead. Ideal for teams without DevOps capacity.
Weaviate (self-hosted or managed) offers hybrid search (vector plus keyword) out-of-the-box – a game changer for German specialist texts where exact terms count. According to Weaviate benchmarks, hybrid search reduces retrieval errors by up to 30 percent. Self-hosting costs you around 150 to 300 euros per month (AWS m5.xlarge with 16 gigabytes of RAM), but you retain full data control – important for GDPR-sensitive use cases.
Milvus (open source) scales horizontally and, according to its own tests, manages over 25,000 queries per second with 100 million vectors. Perfect for extremely large databases, but setup takes 2 to 3 days and requires Kubernetes expertise. Costs: pure infrastructure, plan 500 to 1,000 euros per month for productive GPU clusters.
Qdrant combines Rust performance with Python usability. Particularly strong in filters (metadata-based narrowing before vector search), which enables retrieval precision to be increased by up to 20 percent (source: Qdrant blog). Managed from 50 euros per month, self-hosted with minimal resource footprint.
Decision matrix:
- Fastest start: Pinecone (managed, no setup)
- Best German text search: Weaviate (hybrid search)
- Largest scaling: Milvus (horizontal scaling)
- Best metadata filter: Qdrant (Rust engine)
💡 Tip: Start with Weaviate Managed (14-day free trial), migrate to self-hosted later if necessary. This will save you valuable setup time in week 2 and give you flexibility.
60-minute setup productive Weaviate instance:
- Create an account with Weaviate Cloud (weaviate.io)
- Create cluster (starter tier: free of charge up to 10,000 objects)
- Copy API key, install Python client:
pip install weaviate-client - Define schema (example: document class with title, content, timestamp)
- Upload first batch (100 test documents)
- Test hybrid query:
client.query.get("Document").with_hybrid("AI strategy").do()
After 60 minutes, you have a functional, production-like instance – not a theory, but a system that answers queries.
Day 11-13: Selecting and benchmarking embedding models
Your embedding model is the invisible bottleneck: bad embeddings mean irrelevant retrieval results, no matter how good your LLM is. The MTEB leaderboard (Massive Text Embedding Benchmark) shows rankings – but beware: top scores do not automatically mean best domain fit.
Interpret MTEB correctly:
OpenAI text-embedding-3-large leads with 64.6 points (as of January 2025, source: MTEB leaderboard), but: test set is English-dominated. For German specialist texts, specialized models regularly perform better. multilingual-e5-large (Microsoft) achieves 58.2 points, but according to its own tests shows 15 percent higher relevance for German legal and medical texts than OpenAI models.
What really works for German content:
- OpenAI
text-embedding-3-small: 1,536 dimensions, $0.02 per 1 million tokens. Fast, inexpensive, solid for general topics (marketing, HR, product documentation). - Cohere
embed-multilingual-v3: 1,024 dimensions, explicitly trained for 100 languages, incl. German colloquial language. Costs: 0.10 dollars per 1 million tokens – more expensive, but measurably better for customer support tickets (approx. 12 percent higher Retrieval@10-Accuracy according to Cohere benchmark). intfloat/multilingual-e5-large(open source, Hugging Face): Free of charge, self-hosted on GPU (approx. 8 gigabytes of VRAM). Ideal for data protection-critical projects – GDPR-compliant, as no data reaches external APIs.
Fine-tuning: when it makes sense
Fine-tuning is worthwhile if your Retrieval@10 value remains below 60 percent despite optimization. Example: Technical documentation with highly specific jargon (e.g. mechanical engineering standards). According to studies by Hugging Face, domain-specific fine-tuning increases retrieval accuracy by 10 to 25 percent – but: you need at least 1,000 labeled query-document pairs and 10 to 20 hours of GPU training (costs: approx. 50 to 100 euros).
Performance test: Measure Retrieval@k yourself
Build a test set of 50 real user queries and manually mark the top 3 documents that should contain the answer. Then measure:
- Retrieval@5: How regularly is at least one relevant document in the top 5?
- Retrieval@10: How regularly in the top 10?
- Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR): At what position does the first relevant document appear on average?
💡 Tip: Use this Python snippet for quick
Week 3: LLM integration and pipeline orchestration
Now it gets concrete: You connect your retrieval pipeline with a Large Language Model and orchestrate both components into a functioning RAG system. This week you will decide which LLM generates your answers, how to avoid context overload and how to keep your knowledge base up to date automatically.

Day 15 to 17: Selecting and connecting generator LLMs
The choice of your generator model determines the response quality, costs and latency of your system. OpenAI GPT-4 provides the most accurate answers, but costs up to 0.06 euros per 1,000 input tokens according to the official price list (as of January 2025). Anthropic Claude 3 offers a larger context window of up to 200,000 tokens – ideal if you need to process numerous retrieval results.
Open source models such as Llama 3 or Mixtral reduce API costs to zero, but require their own GPU infrastructure. Expect to pay around 500 to 800 euros per month for an A100 GPU instance on AWS or Google Cloud. To get started, we recommend OpenAI GPT-4-Turbo due to its fast integration and reliable performance.
API limits and practical constraints
Plan with rate limits and token budgets right from the start. By default, OpenAI allows 90,000 tokens per minute in the Tier 1 account – with ten parallel requests with 2,000 token contexts each, that’s a maximum of 45 requests per minute. Implement retry logic with exponential backoff and monitor your token usage daily.
Streaming responses drastically improve the user experience: users see the first response fragments after around 500 milliseconds instead of three to five seconds. Implementation via server-sent events or WebSockets takes a maximum of four hours – the UX improvement is worth the effort.
Prompt engineering for productive RAG systems
Your system prompt is the instruction manual for your LLM. A functioning RAG prompt contains four elements:
- Role clarity: “You are an accurate technical documentation assistant.”
- Retrieval context handling: “Answer based on the following documents only.”
- Obligation to cite sources: “Always state the source document ID at the end.”
- Uncertainty communication: “Say explicitly if the documents do not contain an answer.”
💡 Tip: Test system prompts with ten typical user queries and measure how regularly the model hallucinates or invents sources.
Day 18 to 19: Orchestrate retrieval and generation
The architecture of your RAG pipeline determines latency and response quality. Sequential RAG – first retrieval, then generation – is simple and works for 80 percent of all use cases. Iterative RAG retrieves documents several times if the first response is incomplete – this increases latency by a factor of two to three, but measurably improves complex responses.
Context window management becomes critical when your retrieval returns 20 documents of 500 tokens each. Ten thousand tokens of context cost around 0.30 euros with GPT-4 – with one hundred queries per day, this adds up to 900 euros per month. Limit retrieval results to the top 5 documents or implement a re-ranking layer.
When re-ranking reduces your costs
A re-ranking model such as Cohere Rerank or a fine-tuned cross-encoder re-sorts your initial top 20 retrieval results and selects the most relevant five. Costs: approx. 0.002 euros per query. Savings: up to 60 percent of the LLM context costs. Re-ranking is worthwhile from around 500 queries per day.
LangChain offers ready-made orchestration patterns, but comes with overhead – ideal for prototypes, regularly too abstract for production. LlamaIndex focuses on indexing strategies. Custom pipelines with direct API calls remain our favorite for full control and minimal latency.
Day 20 to 21: Automated data update without downtime
Your knowledge base becomes outdated faster than you think – after just seven days, ten to 15 percent of your documents can be outdated. Automate the detection of changes using file hashes or timestamp comparisons. Only changed documents are re-embedded – this saves up to 90 percent of reindexing costs.
Zero-downtime reindexing works via blue-green indexing: You build a new index in parallel to the productive one. Once complete, you switch traffic to atomic. Old indexes are deleted after 24 hours. Duration for 10,000 documents: around four to six hours. Costs: around 15 to 20 euros for embedding API calls.
Versioning as a rollback strategy
Version each index status with timestamp and Git commit hash of the source data. In the event of faulty updates, roll back to the last functioning version in under five minutes. Monitoring alerts should be triggered if the average retrieval precision falls by more than five percentage points or if more than 20 percent of queries fail to find any documents.
With this automated update strategy, your RAG system remains up-to-date without you having to intervene manually – crucial for long-term production operations.
Week 4: Get production-ready
The final week determines whether your RAG system will hold up in live operation or collapse at the first load peak. This is when you bring all the technical components into a production-ready infrastructure that is scaled, monitored and secured.

Day 22 to 24: Set up infrastructure for production
Kubernetes deployment with intelligent autoscaling
Kubernetes is your central orchestration platform for RAG systems. Set up separate pods for embedding services and LLM inference so that you can scale both components independently of each other.
The critical autoscaling parameters:
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) for embedding services: Trigger at 70 percent CPU utilization, scale down after 5 minutes idle time
- Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) for GPU workloads: dynamically adjusts memory limits to token length
- Custom metrics: Queue length in the retrieval pipeline as an additional scaling trigger
A typical setup will cost you between 800 and 2,500 euros per month, depending on the query volume and the cloud infrastructure selected (AWS EKS, Google GKE or Azure AKS).
Sizing GPU resources correctly
NVIDIA T4 or L4 GPUs with 16 gigabytes of VRAM are usually sufficient for embedding models. For LLM inference with models with 7 billion parameters or more, you need at least A10G or A100 GPUs with 24 to 40 gigabytes of VRAM.
Benchmark rule for dimensioning: Test with 10,000 synthetic queries over 60 minutes. Your system is recommended to keep latencies below 2 seconds for 95 percent of the requests – even at peak load.
API gateway as a protective shield
Your API gateway is the first line of defense against overload and abuse. Rely on proven solutions such as Kong, Traefik or AWS API Gateway.
Essential features for RAG systems:
- Rate limiting: 100 requests per minute per API key as standard, higher limits for premium users
- JWT authentication: Secure token validation with automatic rotation every 24 hours
- Circuit Breaker: Automatic failover in the event of backend failures after 5 consecutive errors
- Request Validation: Schema-based input check against prompt injection and oversized payloads
💡 Tip: Implement request caching for identical requests. This reduces LLM costs by 20 to 35 percent in typical customer service scenarios.
Backup and disaster recovery strategy
Your Vector Database needs a multi-level backup concept. Rely on automated snapshots every 6 hours plus a daily full backup to a separate storage system.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is recommended to be less than 2 hours, Recovery Point Objective (RPO) a maximum of 6 hours – this means that in the worst case, you will only lose the data from the last 6 hours.
Day 25 to 26: Implement observability and monitoring
Metrics that really count
Forget vanity metrics. These four KPIs show you the real system status:
- End-to-end latency (P50, P95, P99): How long does it take from user request to complete response? Target: P95 under 3 seconds
- Retrieval Recall@k: How many relevant documents end up in the top 5 results? Benchmark: at least 85 percent recall
- User feedback score: thumbs up/down after each answer. Track the approval rate daily
- Token costs per request: Average LLM API costs. Monitor outliers that exceed your budget
Practical implementation: Use Prometheus for metrics collection, Grafana for dashboards and a time series database like InfluxDB for historical analysis.
Logging strategy without data garbage
Log in a structured way in JSON and focus on these essential events:
- Query input and retrieved chunks: Which documents were found for which query?
- Generated response: Complete LLM response with timestamp and model version
- Error traces: Stack traces for failures, including retry attempts
- Performance breakdowns: individual times for embedding, retrieval, re-ranking, generation
What you should NOT log: Personal data without explicit consent, production API keys or redundant debug information.
Store critical logs for at least 90 days, aggregated metrics for 12 months. This fulfills typical audit requirements.
Alerting rules: When you need to intervene
Set up alerting thresholds that signal real problems, not every micro anomaly.
Critical alerts (immediate action):
- P95 latency over 5 seconds for more than 5 minutes
- Error rate over 5 percent within 2 minutes
- Vector-DB not accessible or read-only
- GPU OOM error with LLM inference
Warning alerts (observation within 24 hours):
- Retrieval recall falls below 80 percent
- Token costs increase by more than 30 percent compared to 7-day average
- Queue length over 500 waiting requests
Use PagerDuty, Opsgenie or Alertmanager for intelligent escalation. On-call rotation reduces burnout in the team.
A/B testing for continuous improvement
Systematically test new chunking strategies, embedding models or prompt variants against your production baseline. Allocate 5 to 10 percent of traffic to experiments.
Measurable test criteria:
- User satisfaction score (explicit feedback)
- Click-through rate on suggested links
- Time-to-resolution for support tickets
- Cost-per-query
Run tests for at least 7 days to capture weekend effects. Rollback immediately in case of negative results.
Practical example: Customer service RAG at a medium-sized SaaS company
This case shows how a RAG system proves itself in reality: A German SaaS company with 150 employees built a productive system in 28 days – and reduced support tickets by 43 percent.
Initial situation and target definition
The company managed 12,000 support articles in various formats: Markdown docs, PDFs, internal wiki pages and Jira tickets. Every week, 500 new requests were added, which three support employees could barely cope with.
The specific goal: to eliminate 40 percent of repetitive tickets through self-service. The financial framework conditions were clear: a maximum budget of EUR 2,500 per month for infrastructure and API calls, amortized within six months through savings in personnel costs.
Technical decisions and architecture
The team opted for a self-hosted Weaviate server on a dedicated vServer with 16 gigabytes of RAM and 4 CPU cores – at a cost of 89 euros per month. OpenAI Ada-002 was used as the embedding model, combined with GPT-4 for response generation.
The chunking strategy followed a pragmatic approach:
- 300 tokens per chunk as the default size
- 50 tokens overlap between consecutive chunks
- Metadata tagging by product area, timeliness and complexity level
The hybrid search implementation proved to be particularly effective: the system combines vector search with classic keyword search in a ratio of 70 to 30, resulting in a measurable increase in precision and recall – especially for technical terms that semantic embeddings alone cannot reliably capture.
Lessons learned and optimizations
The first embedding model failed spectacularly. The team started with a German open source model that performed well in the MTEB benchmark. In practice, however, it delivered irrelevant results for product-specific queries – the recall was below 60 percent.
The switch to Ada-002 brought the breakthrough: recall rose to 87 percent, and the additional API costs of around 180 euros per month were negligible compared to the benefits. An important insight: benchmark rankings do not automatically correlate with domain performance – own tests are indispensable.
Further optimizations after four weeks of live operation:
- Re-ranking layer with a cross encoder increased precision by 12 percentage points
- Automatic feedback loop: users mark helpful answers, this data flows into weekly retrieval audits
- Fallback mechanism: if the confidence score is low, the system automatically forwards users to human agents
After three months, the system reached the original target: 43 percent fewer tickets, average response time under three seconds, user satisfaction at 4.2 out of 5 stars. The ROI was already positive after four months – two months faster than planned.
You now have the complete blueprint for a productive RAG system – from initial data collection to scalable live operation. 30 days is realistic if you prioritize consistently: a clean database before fancy features, pragmatic tool selection before perfectionism, continuous testing before blind trust in benchmarks.
The most important levers for your success:
- Start seriously with week 1: 70 percent of all RAG problems are caused by poor data quality, not by the wrong choice of technology
- Test embedding models with real user queries: MTEB rankings are a guide, not a guarantee for your specific domain
- Implement monitoring from day 1: retrieval recall and token costs show you immediately where your system is weak
- Schedule automated updates: a knowledge base without updates is useless after four weeks
- Use hybrid search for German specialist texts: The combination of vector and keyword search measurably increases precision by 15 to 30 percent
Your next concrete steps:
Choose a use case with a clear ROI today (customer service, internal document search or compliance queries). Reserve four continuous weeks in your calendar – RAG projects fail due to interruptions, not complexity. Start with a managed service like Weaviate Cloud or Pinecone to save setup time.
RAG systems are no longer a future project – they are the standard for any company that wants to use its internal knowledge productively. The technology is mature, the tools are available, the business cases are proven.
The only question is: when do you start?