The release of Tencent’s Hunyuan-Large model marks an important milestone in the field of large-scale language models. This innovation is not only technically impressive, but also shows how openly available code can increase the speed of innovation in AI research.
Innovations and architecture
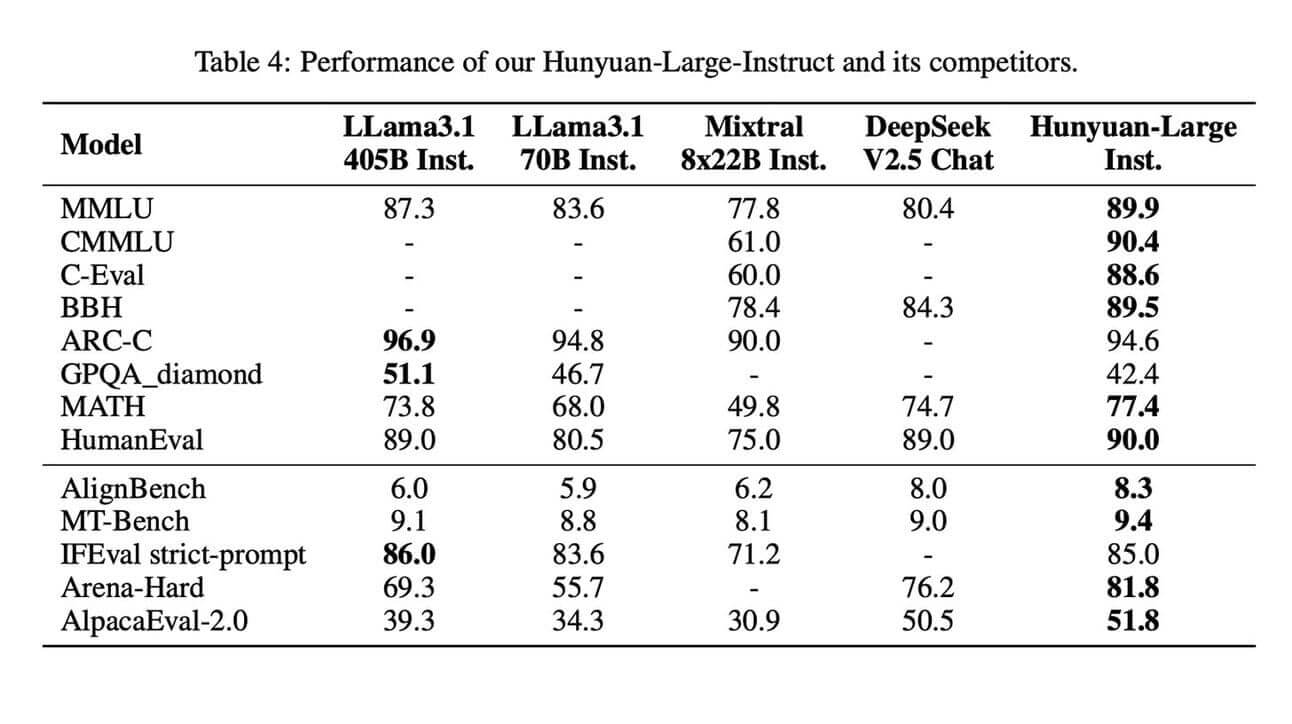
The Hunyuan-Large model is based on a Transformer-supported Mixture of Experts (MoE) approach, which allows it to scale efficiently by activating only a subset of the 389 billion parameters for input at a time. This not only reduces computational costs, but also improves model performance in tasks of language understanding, generation, reasoning and more. With 52 billion activated parameters, it is the largest open MoE model of its kind, outperforming powerful models such as the LLama3.1-70B.
A major technical advance is the use of greatly augmented synthetic training data, which significantly increases the performance of Hunyuan-Large. This is complemented by an innovative mixed expert routing strategy that ensures optimal input distribution and a key-value cache compression method that reduces memory consumption.
Availability and legal considerations
Hunyuan-Large is publicly available to encourage further development in the AI community. While the disclosure of such large models raises questions about intellectual property rights, it also enables new discussions about the future creation of specific legal frameworks. Geographical restrictions, such as the exclusion of the European Union from certain usage rights, also open up space for legal debates in international AI governance.
The publication of a model of this scale raises the potential to influence future research and practical applications in natural language processing extensively. The balance between open access and legal protection is a critical discussion that requires adaptations to existing and new developments.
Implications and discussion
Hunyuan-Large has the potential to redefine research in various scientific and industrial fields. Professional discussions could focus on the technical solutions behind the successful scaling of such models. Most notably, extensive training data and specialized learning rate adaptation strategies will enable further optimizations in the development of future open-source models.
The most important facts about the update:
- Largest open MoE model with 52 billion parameters enabled.
- Performance exceeds existing models through new data and routing techniques.
- Promotion through open access, but with geographical restrictions.
- Focus on legal issues around copyright and intellectual property.
- Potential reinvention of research and applications in native language processing.
Sources: Arxiv