Cursor is an IDE for developers that fully supports AI. The Cursor 2.0 update brings autonomous AI agents for coding and lightning-fast execution using the proprietary AI model Composer.
Summary: What’s new in Cursor 2.0?
- Efficient multi-agent coding: Up to eight specialized AI agents work on code projects in parallel and in isolation.
- Own high-performance model: Composer uses low-latency processes to ensure fast execution – usually under 30 seconds.
- Secure and collaborative environment: Sandbox terminals and real-time collaboration improve security and teamwork.
- Practical application: Cursor 2.0 is suitable for developers, teams and companies that value speed and efficiency in complex tasks.
- Versatile technology support: Python, TypeScript, JavaScript, Go, React, Next.js and other tools can be used with ease.
Read also: Claude Sonnet 4.6: The massive coding & agent update
Multi-agents and Composer: new speed in coding
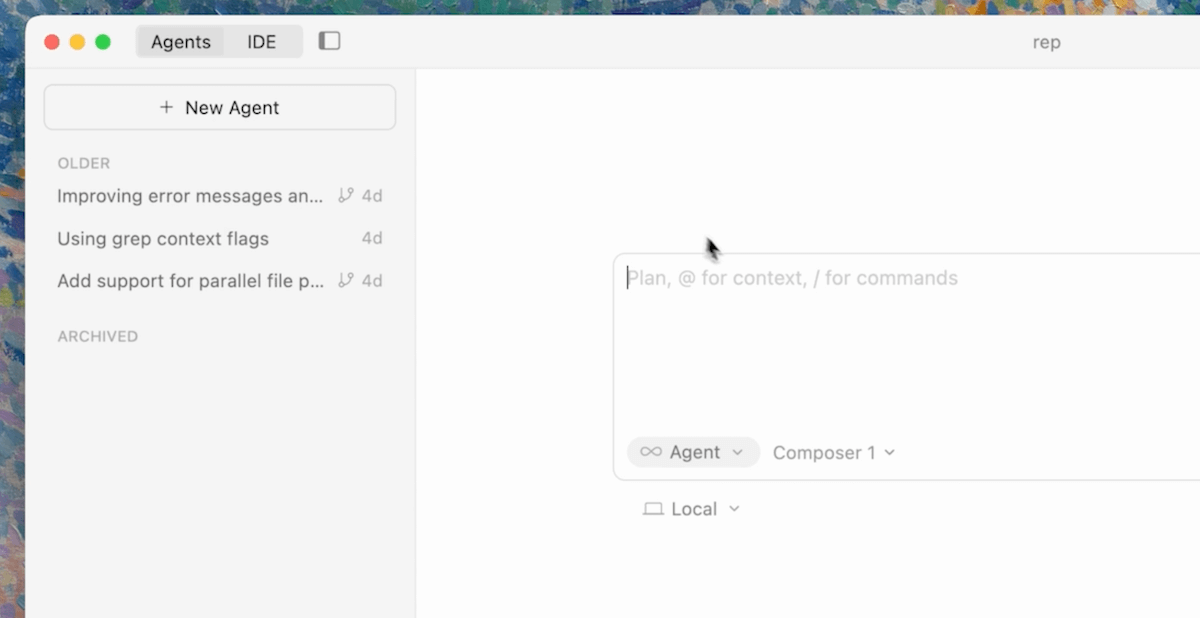
Cursor 2.0 integrates up to eight AI agents that perform tasks in parallel in separate worktrees or on remote machines. This enables high scalability and promotes efficient work on large projects. Thanks to the structurally separate workspaces, the code base remains stable, even if different agents are searching for bugs, programming features or carrying out tests at the same time.
Official video of the Cursor 2.0 update:
Composer: The fast, independent AI model
Composer, Cursor’s in-house AI model, is characterized by extremely fast task execution – according to the manufacturer, the model is around four times faster than competing solutions and usually processes tasks in less than 30 seconds. Composer does not require a connection to external services such as OpenAI, which increases sovereignty over company or customer data.
New workflows: Automated tests and code review in the editor
With the native browser, automated tests can be carried out directly in the editor and iteratively in the project context. The new agent-based user interface dispenses with file-based navigation; each task is given a clear, isolated area. The code review window summarizes changes precisely, which supports quick releases and continuous improvements in the development process.
New interface for multi-agent feature
The multi-agent feature supports a wide range of scenarios: Bug diagnosis and troubleshooting, simultaneously with feature development. For example, one AI agent can find errors in a Python project while a second AI agent implements complex TypeScript components. This makes teams more efficient, as tasks are parallelized and test cycles are significantly streamlined.

FAQ: Frequently asked questions
- What is Cursor 2.0?
An AI-supported development environment with multi-agent architecture and its own AI model Composer for efficient, parallel coding. - Which programming languages are supported?
Python, TypeScript, JavaScript, Go, React, Next.js, HTML, CSS, PHP, Java, C#, TensorFlow, PyTorch and many more. - Can multiple developers work with Cursor at the same time?
Yes, there is real-time collaboration with multiple team members and AI agents per project. - How does Cursor 2.0 contribute to safety?
Each AI agent has an isolated sandbox terminal that prevents interference and unintentional overlaps. - How fast does the Composer AI model work?
Typical tasks are completed in under 30 seconds, Composer is approximately four times faster than comparable solutions.
Conclusion: Cursor becomes more efficient, faster and helps with integrated code reviews
Cursor is a sophisticated development solution for start-ups, development teams and agencies that need to develop complex web applications with React, Next.js or Go and deliver them in a timely manner. Cursor 2.0 is a modern solution, especially for projects that require frequent, fast iterations and automated tests. The update now brings:
- AI-powered coding with a focus on speed and parallelization through multi-agents.
- Composer enables fast, independent and safe task execution.
- Optimized workflows through automated tests and code review directly in the editor.
- Support for all common programming languages and collaboration features.
Further sources